NCD Policies and Plans
Overview
In the South-East Asia Region, NCDs cause an estimated 9 million deaths annually, almost half of them premature. Since 2014, preventing and controlling NCDs has been a Flagship Priority in the Region. This enabled NCDs to be prioritized in the agendas of ministries of health and development partners and reinforced WHO country offices’ focus. With the advocacy and support through Regional Flagship, all Member States have aligned the 2025 NCD national targets with the global voluntary targets and have committed to the UN Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) target 3.4 on reducing premature mortality from NCDs.
The Action plan for the prevention and control of noncommunicable diseases in South-East Asia Region, 2013–2020, extended to 2030, contains good guidance and actions, and will remain the basis of the regional NCD response.
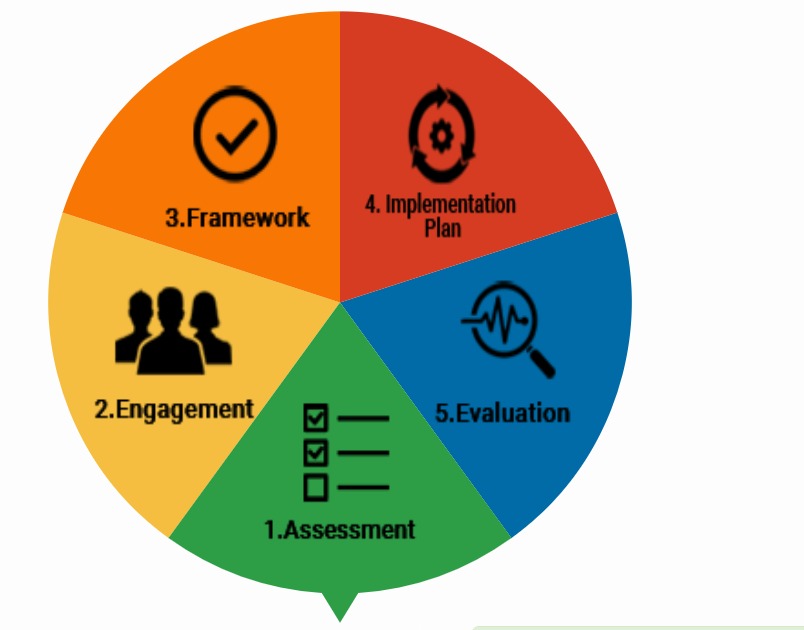
The toolkit for developing a multisectoral action plan is a “how to” guide for developing, implementing and evaluating a multisectoral action plan for prevention and control of NCDs. It is targeted at policy-makers, planners and programme managers, and is intended to help countries, provinces and cities meet the requirements for achieving global and national NCD targets and the Sustainable Development Goals. NCD Multisectoral action plan
n order not just to sustain but to accelerate progress, at the Seventy fourth Session of the WHO Regional Committee, Member States requested WHO to develop the Implementation roadmap for accelerating the prevention and control of NCDs in South-East Asia 2022–2030.