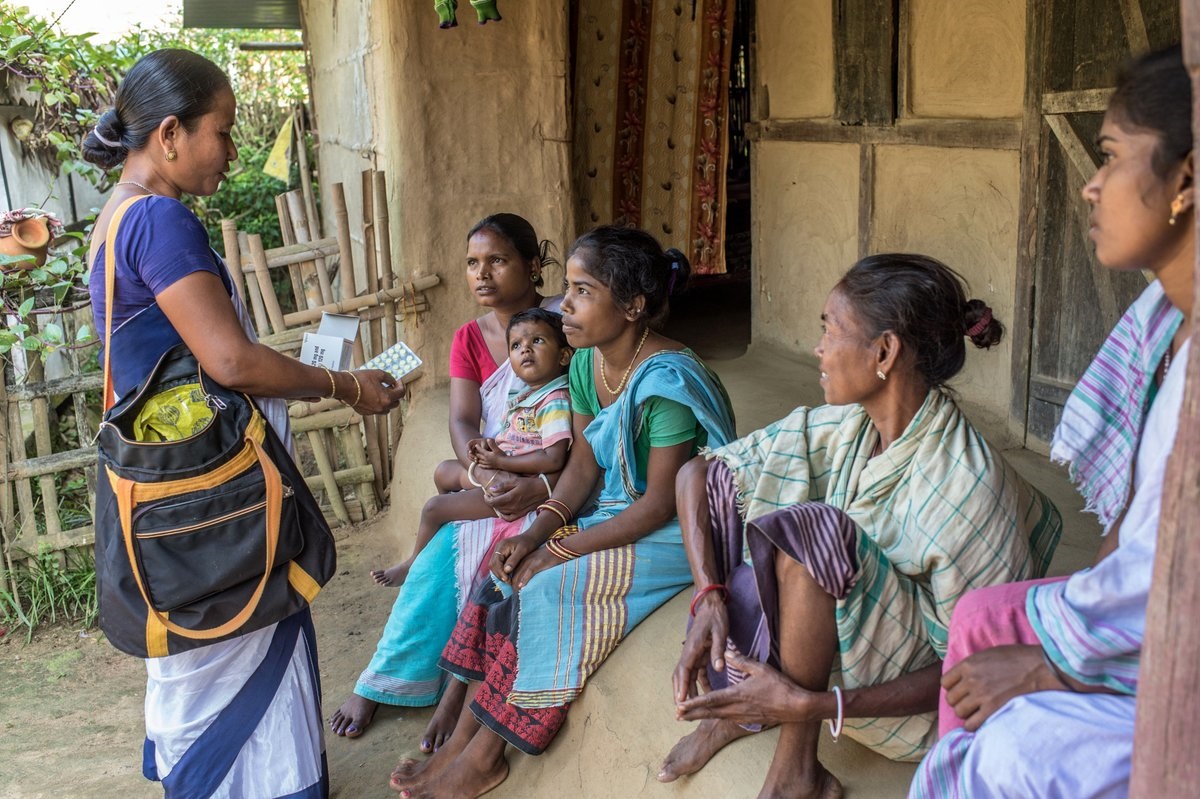Universal health coverage in the South-East Asia
Universal health coverage (UHC) is about ensuring all people get
the quality health services they need, without experiencing financial hardship.
UHC is central
to achieving progress on the Sustainable Development Goal (SDG) 3.
UHC has two dimensions – access to needed health care, and
financial protection. The Regional average for the UHC essential health
services index is 61% in 2019 compared with 46% in 2010. On the other hand,
over 65 million people are pushed into poverty because of health expenditure.
Sound health policies and health financing strategies are essential,
to ensure that no one is impoverished as a result of the costs of health care,
and that the resources are used efficiently and fairly.
As countries strive to attain universal health coverage they
must be able to measure and monitor their progress and have robust
accountability mechanisms in place.
Moving towards UHC is a gradual process, and every country has committed itself to do so.
The Department of UHC/Health Systems (HSD) supports
Member States with improving their health systems towards achieving universal
health coverage. UHC is one of WHO's flagship initiatives in the South-East
Asia Region with a focus on the health workforce and access to medicines.
Technical links